Intermediate Reading Course. Section 1: The Basics
Sample Expository Mode of Writing
The article below is an example of a text using the expository, or informative, mode of writing.
Back to the lesson
IMPORTANT NOTE. The information below is highly summarized and presented only as a sample expository mode of writing. Do not rely on it as a source for cell mitosis.
Cellular Mitosis
Mitosis is the process by which a single cell divides into two genetically identical daughter cells. It occurs in almost all organisms and is essential for growth, repair and development. Mitosis includes four distinct stages: interphase, prophase, metaphase, and anaphase.
Interphase
During interphase, the cell grows, replicates its DNA and builds up the proteins it needs for mitosis. Interphase is an important part of the cell cycle and must be completed before the cell can proceed to the next stage.
Prophase
At the prophase stage, the chromatin condenses and the centrosomes replicate. The nuclear envelope then breaks apart and the spindle fibers begin to form.
Metaphase
During metaphase, the chromosomes line up on the equator of the cell and become visible. The spindle fibers attach themselves to the centromere of each pair of chromosomes.
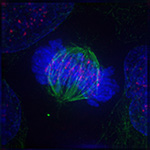
Metaphase
Anaphase
Anaphase is the final stage of mitosis. During this stage, the sister chromatids, which have been held together by a spindle apparatus, separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. This process is known as chromosome segregation. The cytoplasm then divides into two separate cell masses. Anaphase takes place following the metaphase and before the telophase. In this stage, the centriole pairs move to opposite poles of the cell and the nuclear envelope begins to disintegrate.
Back to the lesson